

We define courses as community engagement or service-learning based on the student learning experience and community impact, not the course title. Our broad term for these courses is "Community-Engaged Learning" which classifies the variety of curricular community-based learning experiences and activities that students engage in that contribute to the public good.
Service Learning (CSL) is a specific type of community-engaged learning in which substantive community engagement and the related community partnerships are critical components of course learning, with equal focus on community impact and student learning related to social justice or responsibility. Service-learning courses may also be labeled with a variety of titles.
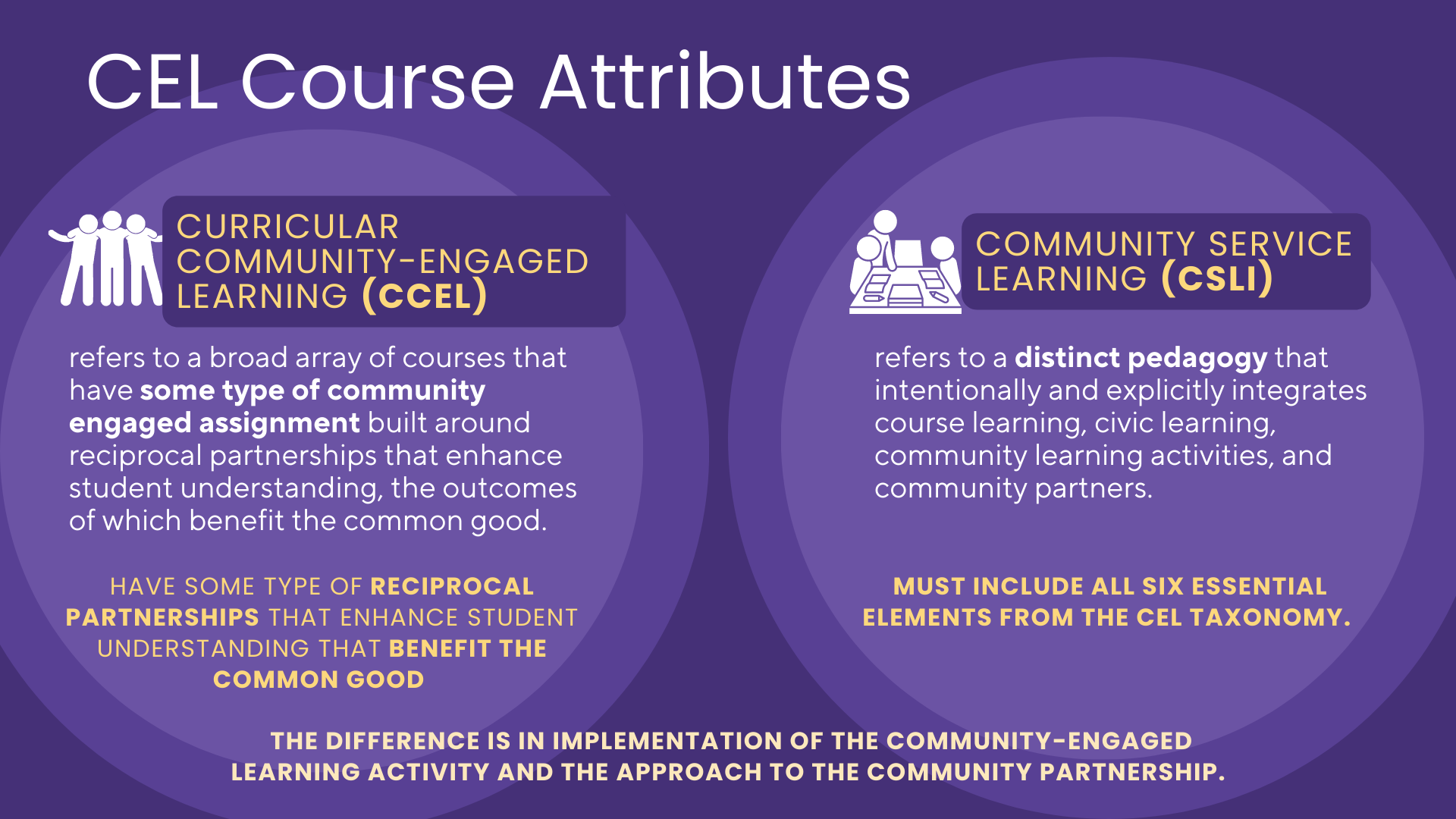
Service Learning is a distinct pedagogy that intentionally and explicitly integrates course learning, civic learning, and community learning activities with community partnerships. It combines academic study in any discipline with community service so that each is enhanced by the other. Through a process of structured reflection, the service experience is integrated with the lessons of the classroom to enrich learning outcomes. Students enrolled in a course offering a community service learning opportunity balance their time between classroom instruction, service in the community, and reflection upon their service experience. The service experience may include direct service to people in need, applied research, community outreach, education, or policy analysis and advocacy. Student learning outcomes relate directly to the service experience and their reflections on that experience. More specifically, CSLI Courses:
-
Involve students in service activities or projects that are responsive to community needs. Students who choose the CSLI option must complete no less than 20 hours per academic term of direct academically relevant community service.*
-
Include academic topics that directly address questions related to the activities of the students.
-
Require student reflection on the interrelationships between course content, concepts, objectives, and community-based learning activities
At this time, courses that are designated as CSL are attributed as CSLI at the course section level every semester. CSL service hours confirmed by and uploaded into the SF Gateway (Campus Solutions) during the grading period by faculty will be recorded in a student's official transcript. Faculty looking for more information, please visit our CSLI & CCEL Attribute Guide
Curricular Community Engaged Learning (CCEL) refers to courses in any discipline that have some type of community-engaged experiences and activities built around reciprocal partnerships to benefit the common good and enhance student learning.
Collaborative project goals and priorities are driven by community partners and negotiated with faculty and students involved in the CEL opportunity. Collaborative projects may focus on improving community resources or capacities, participatory or action research projects, or implementing a range of other activities to advance community-identified goals and strategies. A course is considered ‘community-engaged’ based on implementation, not a title or course label. Within CEL, practices vary widely in terms of depth, breadth, and scope of student activities and partnerships. CEL courses may use such terms as fieldwork, applied, practicum, internship, and service
At this time, courses that are designated as CSL are attributed as CSLI at the course section level every semester. CSL service hours confirmed by and uploaded into the SF Gateway (Campus Solutions) during the grading period by faculty will be recorded in a student's official transcript. Faculty looking for more information, please visit our CSLI & CCEL Attribute Guide
CSL and CCEL are identified as high-impact educational practices (HIP) by the Association of American Colleges and Universities (AAC&U). Faculty and staff members are integral to service-learning by serving as Community Service Learning (CSL) course instructors, departmental program coordinators, and advocates to students. In addition, faculty and staff members play vital roles in engaging students in critical reflection, interacting with community partners, and conducting community-based research. CSL courses promote student success and retention while improving the quality of learning in traditionally underserved student populations, including students of color, the economically disadvantaged, first-generation college students, and students with different learning styles.
In addition, research shows that CSL and CCEL have beneficial impacts on faculty, students, and organizations involved in collaborative, experiential learning:
- Impacts for faculty include increased satisfaction with the quality of student learning, increased commitment to research
- More lively class discussions and increased student participation
- Increased student retention of course material
- Increased student awareness of community and "real world" issues
- Increased opportunities for research and publication
- Increased faculty awareness of community issues
- Impacts for students include improved learning outcomes, personal growth and professional development
- Increased pro-social activities
- Enhanced relationships with the university
- Improved graduation rates.
Students enroll in CSL and CCEL courses by following the regular methods described in the Class Schedule. CSL and CCEL courses may be offered in any discipline, degree program, and by any department or program on campus. Undergraduate and graduate courses are eligible to receive CSL/CCEL designations or attributes.
Academic programs are encouraged to include assessment measures specific to CSL and CCEL courses in the program review process, including documenting any evidence of enhanced student success, whether related to learning outcomes, personal efficacy, retention/graduation, or other program goals. When assessing CSL and CCEL courses, it is important to measure along at least three dimensions:
-
academic learning,
-
civic learning, and
-
community partner goals.
Programs are encouraged to contact ICCE for support and additional resources related to assessing CSL and CCEL courses, including how they contribute to program goals.
Courses may be designated as CSL or CCEL in SF State’s Curriculum Inventory Management (CIM) system. In addition, when multiple sections of a course are taught, each section can receive a different attribution, including whether the CSL or CCEL activities are Required (R), Extra Credit (EC), or Optional (O) for students enrolled in the course, where:
-
R (required): all students enrolled in the course must participate in CSL activities and complete related assignments. CSL is embedded into the course curriculum.
-
EC (extra credit): enrolled students have the option to participate in some or all CSL activities and assignments and will be awarded extra credit for those activities and assignments.
-
O (optional): enrolled students can elect to participate in CSL activities and complete related assignments OR participate in traditional “classroom” activities and complete related assignments.
The CSU Chancellor’s Office provides a Community-Engaged Learning Tool (CELT) designed for CSU faculty to identify where a course falls along the spectrum of CEL. The CEL Tool asks faculty a series of questions based on the CSU-CEL Taxonomy and results in the assigning of an attribute. The CEL Tool is meant to allow the CSU to capture meaningful data across the system to better support faculty and work towards appropriate recognition for this work. It also offers insight into curriculum preparation and design that take into consideration essential elements along the community-engaged learning spectrum that help shape and improve student learning. Completing the CELT provides faculty with an opportunity to reflect on where they are and ways they can further improve and/or enhance their community-based teaching and strengthen their community partnerships.


Community Engaged Learning Tool (CELT)
Once you have reviewed the CEL Essential Elements Taxonomy, begin taking the CELT for your course!
View: CELT Questions (PDF)
Department Guide for Community Engaged Attribute
This document is a resource for departments and faculty on moving a course through Course Leaf

Community Engaged Learning Essential Elements
Click the link below to view the Community Engaged Learning Essential Elements Interactive Roadmap

How to Complete the CELT Tutorial
Brought to you by the CSU Center for Community Engagement
Frequently Asked Questions
Academic Senate Policy #S22-224, Designation Policy for Community Service Learning Courses
Current (supersedes Policy # S03-224) Senate Approval: 5/03/2022 [Presidential Approval: 5/06/22]
Abstract
This policy seeks to provide definitions and policy, in accordance with guidance from the Chancellor’s Office, on the process for designating various types of community service or community-engaged courses.
Summary
As part of the Chancellor’s Office (CO) 2018-19 California’s Call to Service Initiative, the CO identified an accountability goal to strengthen system-wide data collection infrastructure around community-engaged courses (as defined by the Chancellor's Office Center for Community Engagement). The purpose is to improve data collection to better support faculty and understand student learning, faculty efforts, and community impact. All campuses must implement two system-wide course attributes (community service learning and community-engaged learning) in the course management system to effectively identify and track these types of courses. Campuses are also required to distinguish service learning, as a distinct pedagogy, from community-engaged learning, which can include a variety of community-based learning experiences. A working group consisting of representatives from the Chancellor’s Office, CSU campuses, and the CSU Academic Senate developed the tools and resources needed for this initiative. The Institute for Civic and Community Engagement (ICCE) is overseeing this effort for San Francisco State University, including the dissemination, tracking, assessment, and reporting of the survey and survey data.
Community service learning (CSL) and community-engaged learning (CEL) include a range of high-impact pedagogical practices that enhance students’ learning and foster civic understanding through active course-based learning that involves meaningful collaboration with community partners. The academic study may be in any discipline or combination of fields. Student learning outcomes benefit the common good, whether through direct service to communities in need or the organizations that serve them or through indirect service projects that contribute to community capacity building more broadly. CSL and CEL enhance academic learning by allowing students to make connections between their classroom education and its application to the field. These high-impact learning experiences help students to clarify their career goals and acquire work-related skills, develop a heightened sense of civic responsibility and awareness of moral and ethical issues, and provide them with a wide variety of work options with the goal of being value-added for the community they serve. Working from a common understanding will further the university’s identity as an “engaged institution,” contribute to quality transparent learning experiences for students, and offer opportunities for faculty dialogue and scholarship within and across disciplines.
Academic Senate Policy: Course Designation
The attributes are applied in the student information system and based on a CEL Tool (CELT) that asks faculty about their teaching and community partnershipii practices. The CELT is based on a course taxonomy for community- engaged learning which outlines the essential elements of these types of courses within a spectrum of implementation practices. Faculty complete a separate CELT for each course and the attribute is applied based on the faculty member’s responses.
Both Curricular Community-Engaged Learning and Service Learning are valuable learning tools for students.
The difference is in implementation of the community-engaged learning activity and the approach to the community partnership. This effort is about data collection to better understand student learning, faculty efforts, and community impact so that as a system we can
- better support faculty and community partners; and
- improve evidence-based research of community-engaged learning experiences on student success and its impact on faculty scholarship.
The information will lead to more accurate and easier course reporting and offers the potential for scholarship around community-engaged teaching. SL/CE offices will also be planning on how best to use the information for their campuses.
Faculty will need to complete a separate CELT for each CEL course they teach and should be completed at a minimum of every five years, but it may also be completed anytime there is a significant course change (i.e., a new CEL course developed, significant revisions to the CEL course or change in faculty member teaching the CEL course).
Faculty members who complete the CELT will receive a Confirmation Email with your designated CEL attribute (either CCEL or CSLI). If more information is needed, ICCE will follow up with you.
For course that are currently listed as CSL, ICCE recommends faculty still take the CELT Survey and edit the designated community engagement course attribute if needed.
We acknowledge our faculty who have committed to teaching community-engaged learning courses and greatly appreciate current CSL faculty for completing the CELT tool. It is our intention to use the CELT results to enhance our services to provide faculty with resources to support community-based teaching and strengthen community partnerships. Furthermore, working from a common understanding will further the university’s identity as an “engaged institution,” contribute to quality transparent learning experiences for students, and offer opportunities for faculty dialogue and scholarship within and across disciplines.